Somatosensation
5
Learning Objectives
Know what the somatosensory homunculus is.
Know where you can find primary sensory cortex, and what is different about the neural responses in primary sensory cortex and nearby regions in parietal cortex that also respond when you touch an object.
Be able to describe the effect of attention on neural responses.
The cerebral cortex maintains sensory topography in particular areas of the cortex that correspond to the position of the receptor cells. The somatosensory cortex provides an example in which, in essence, the locations of the somatosensory receptors in the body are mapped onto the somatosensory cortex. This mapping is often depicted using a sensory homunculus.
The term homunculus comes from the Latin word for “little man” and refers to a map of the human body that is laid across a portion of the cerebral cortex. (Fig.2.5.1) below shows the body parts in proportion to the amount of brain space allocated them.
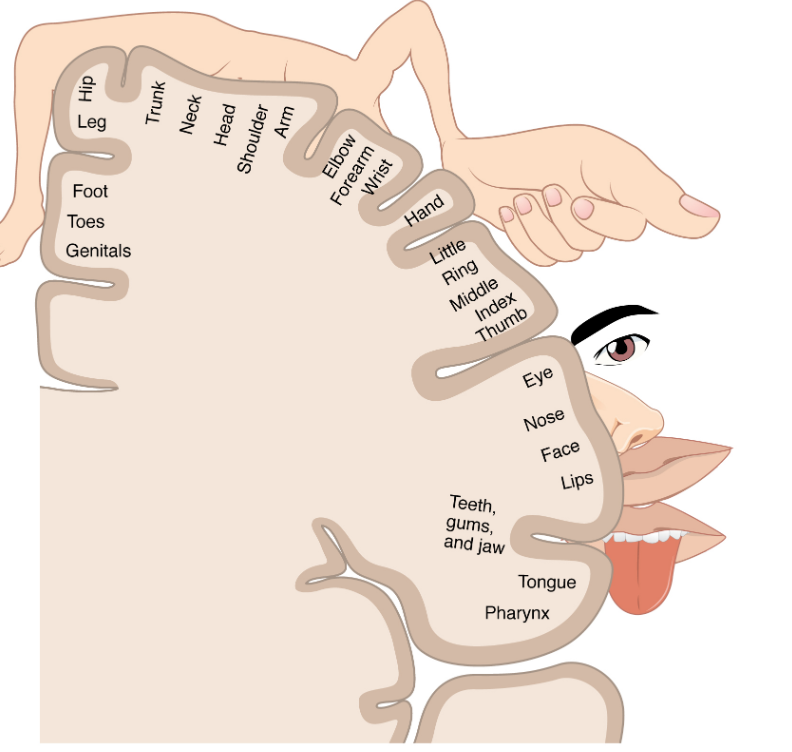
Primary somatotopic representation (S1) is on the postcentral gyrus. It is a distorted map (body parts with high receptor density get more territory). Some senses that are controlled by the primary sensory cortex are touch, thermal information, orientation and direction. Regions in the parietal cortex outside S1 respond to more complex features such as object-selective responses.
Unattended stimuli can fail to elicit neural response, even in primary somatosensory cortex. But the effects of attention are stronger outside S1.
Watch the video linked here and included below to learn more about somatosensory representations in the brain!
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
OpenStax, Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 14.2 Central Processing
Provided by: Rice University.
Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/14-2-central-processing
License: CC Attribution 4.0
Adapted by: Hanna Hoyt
Cheryl Olman PSY 3031 Detailed Outline
Provided by: University of Minnesota
Download for free at http://vision.psych.umn.edu/users/caolman/courses/PSY3031/
License of original source: CC Attribution 4.0
Adapted by: Hanna Hoyt

