Hearing Loss and Central Auditory Processing
53
Learning Objectives
Understand which hearing aids are most effective in what cases of hearing loss and why.
Know the main features of hearing aids.
Be able to discuss the prevalence of hearing aids.
Hearing aids amplify sound, so they rely on functioning hair cells. Hearing aids do not restore normal hearing when used to treat sensorineural loss, because the effects of neural damage are so complicated. Given the mechanical nature by which the sound wave stimulus is transmitted from the eardrum through the ossicles to the oval window of the cochlea, some degree of hearing loss is inevitable. With conductive hearing loss, hearing problems are associated with a failure in the vibration of the eardrum and/or movement of the ossicles. These problems are often dealt with through devices like hearing aids that amplify incoming sound waves to make vibration of the eardrum and movement of the ossicles more likely to occurs.
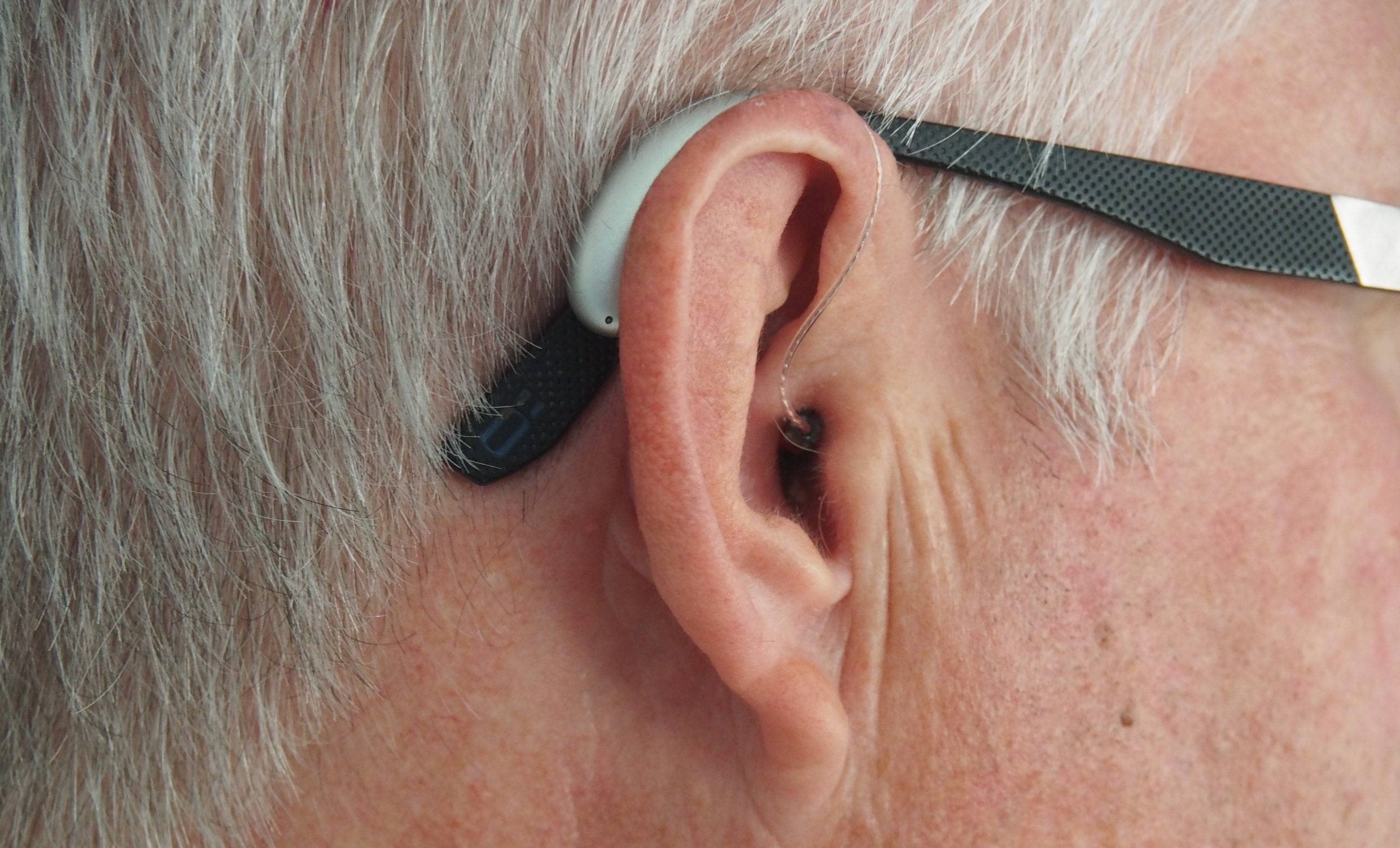
Modern hearing aids have, in addition to basic sound amplification, these features: amplitude compression (mimicking the natural compressive response of the inner ear, which you lose when you lose OHC; this reduces Loudness Recruitment), and noise reduction—a filtering algorithm that tries to take out background noise. Noise reduction improves comfort but doesn’t improve speech intelligibility, and the algorithm doesn’t know which sound you’re trying to pick out and might reduce the wrong sound. Current research is trying to use brain-steering: an EEG signal can detect which speech sound you’re paying attention to, and this can be used to control amplification. Maybe someday.
Only about a quarter of the people who would benefit from hearing aids actually use them. Adoption rates are higher (30-40%) in countries like Norway where insurance covers hearing aids. These low rates may be due to the $2k-$3k price tag that insurance often may not cover. Another thing that keeps adoption rates down is that they really don’t help in all situations. On the bright side, new FDA regulations are coming out that might create over-the-counter hearing aids and bring down the price!
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
OpenStax, Psychology Chapter 5.4 Hearing
Provided by: Rice University.
Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/4abf04bf-93a0-45c3-9cbc-2cefd46e68cc@5.103.
License: CC-BY 4.0
Adapted by: Grace Cumming & Kori Skrypek
Cheryl Olman PSY 3031 Detailed Outline
Provided by: University of Minnesota
Download for free at http://vision.psych.umn.edu/users/caolman/courses/PSY3031/
License of original source: CC Attribution 4.0
Adapted by: Kori Skrypek

