Taste and Smell
30
Learning Objectives
Be able to describe the paradoxical relationship between scent and memory.
Know the distinction between detection and recognition of a scent.
Know whether or not it is a myth that females have a better sense of smell than males.
The strong projections from the olfactory tract to piriform cortex and other regions associated with memory (e.g., parahippocampal gyrus) and emotion (e.g., the amygdala) help us understand why smells readily evoke memories, and why the emotional content of smell-evoked memories is often stronger than other memories (Willander, 2007). However, the relationship is one-directional. While smells evoke memories, we’re not always good at recognizing scents.
When studying detection of scents, there are two kinds of absolute thresholds that can be measured: detection thresholds and recognition thresholds. To measure detection thresholds, the participant is simply answering the question “can you smell something?” To measure recognition thresholds, the participant is answering the question “what can you smell?” Recognition thresholds are typically about 3 times larger than detection thresholds (Van Gemert, 2003).
Have you ever heard that women have a better sense of smell than men? Olfactory anatomy is the same for both sexes, but there is some experimental evidence that females perform slightly better at standardized smell tests than males (Sorokowski, 2019). The effect size is very small; differences in performance are likely related to experience (some bias might occur in testing if one sex is more likely to have experience with test scents than others) and possibly sex hormones.
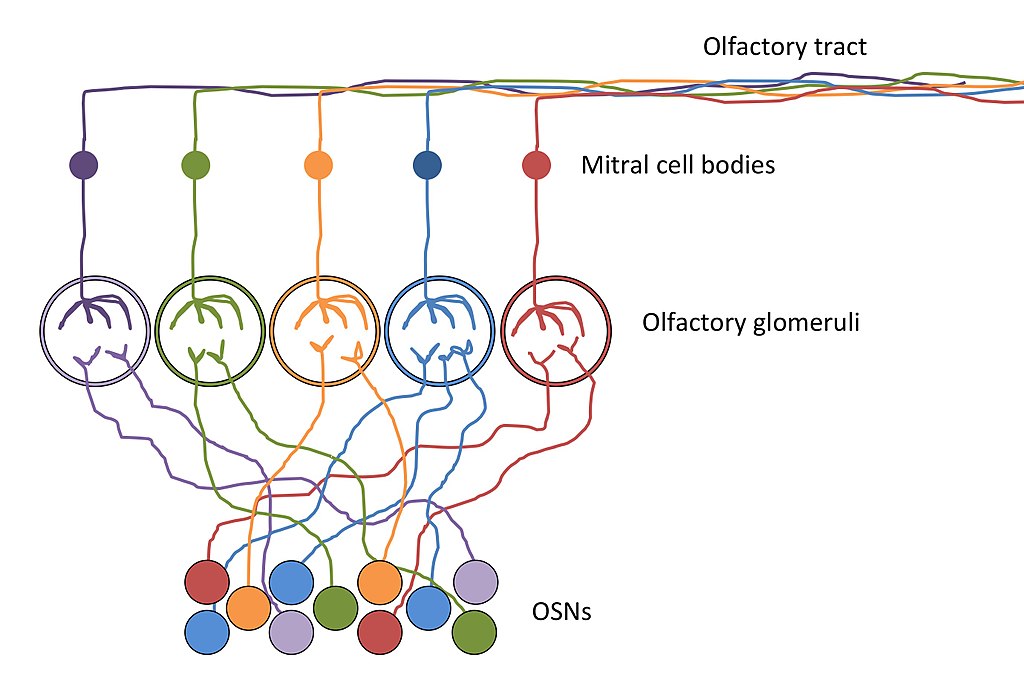
Predicting how something is going to smell to someone is difficult—each molecule activates several different receptors, and each receptor might respond to several different molecules. In addition, most things we smell have several different molecules in them, each of which is going to activate several different receptors. So the olfactory code that goes to the brain is complicated, and each of us has a different set of experiences that means our brain interprets these patterns differently. This interpretation is done in piriform cortex, on the bottom of the temporal lobe (not far from the parts of the brain responsible for forming memories!). We can’t look at a single molecule and predict what it is going to smell like to someone. But we can look at the pattern of responses across mitral cells (which get their information from bundles of synapses called glomeruli), and if the pattern is the same for two scents (for example, in the figure below, lots of action potentials from the orange mitral cell, and a few from the blue one), then the person smelling the two scents will say they smell the same.
Provided by: University of Minnesota
License: CC BY 4.0CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
OpenStax, Biology 2e Chapter 36.3 The Chemistry of Life: Taste and Smell
Provided by: Rice University.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/1-introduction
License: CC BY 4.0
References:
Sorokowski, P., Karwowski, M., Misiak, M., Marczak, M. K., Dziekan, M., Hummel, T., & Sorokowska, A. (2019). Sex differences in human olfaction: A meta-analysis. Frontiers in psychology, 10, 242.
Willander, J., & Larsson, M. (2007). Olfaction and emotion: The case of autobiographical memory. Memory & cognition, 35(7), 1659-1663.
Van Gemert, L. J. (2003). Odour thresholds. Compilations of odour threshold values in air, water and other media. Oliemans, Punter & Partners BV, Utrecht.

