Taste and Smell
32
Learning Objectives
Know the difference between a taste bud and a papilla.
Be able to name the different kinds of papillae.
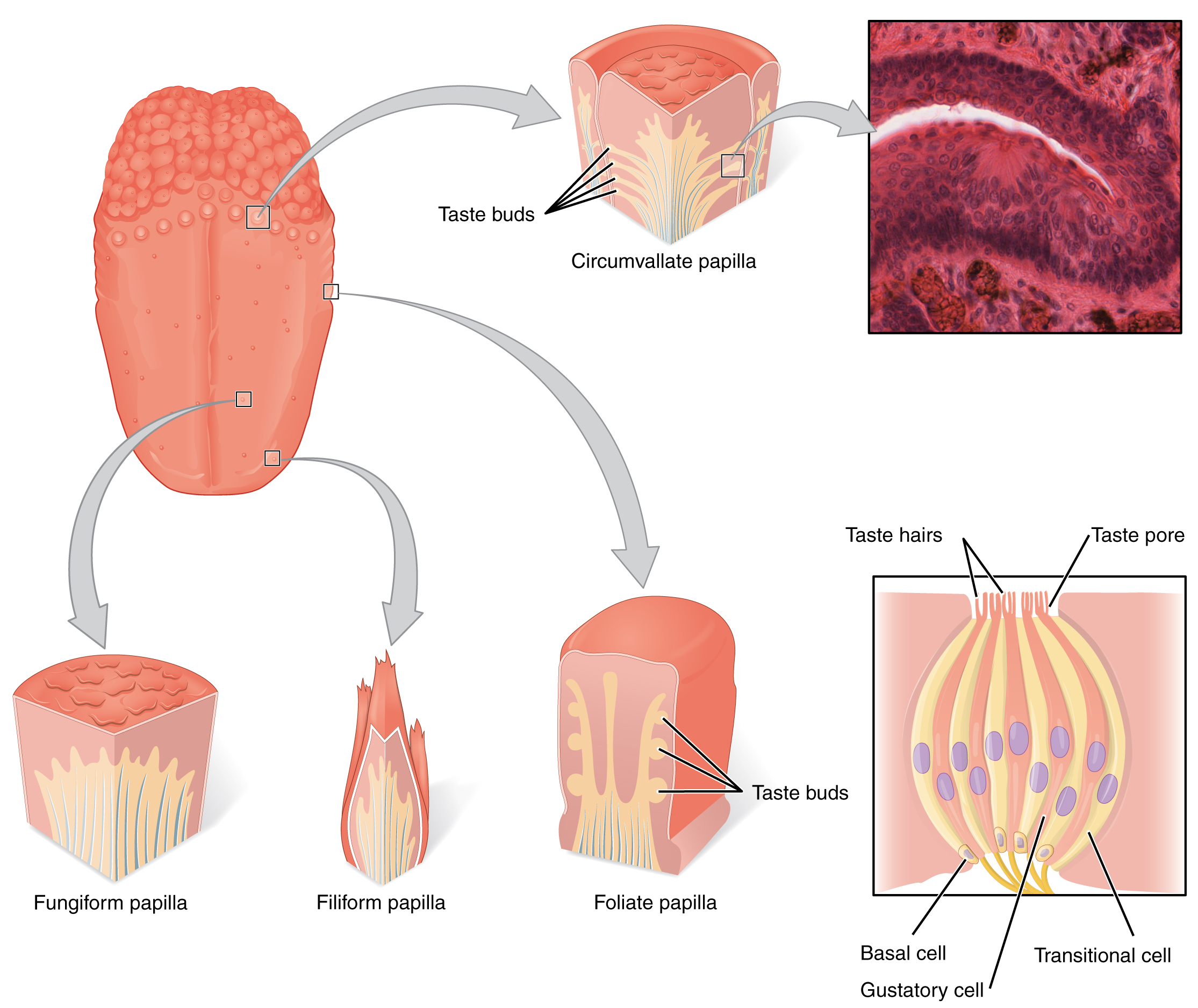
Gustation is the special sense associated with the tongue. The surface of the tongue, along with the rest of the oral cavity, is lined by a stratified squamous epithelium. Raised bumps called papillae (singular = papilla) contain the structures for gustatory transduction. There are four types of papillae, based on their appearance: circumvallate, foliate, filiform, and fungiform (Fig 4.4.1). Within the structure of the papillae are taste buds that contain specialized gustatory receptor cells for the transduction of taste stimuli. These receptor cells are sensitive to the chemicals contained within foods that are ingested, and they release neurotransmitters based on the amount of the chemical in the food. Neurotransmitters from the gustatory cells can activate sensory neurons in the facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus cranial nerves.
Exercises
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
OpenStax, Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 14.1 Sensory Perception
Provided by: Rice University.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/14-1-sensory-perception
License: CC-BY 4.0

