32
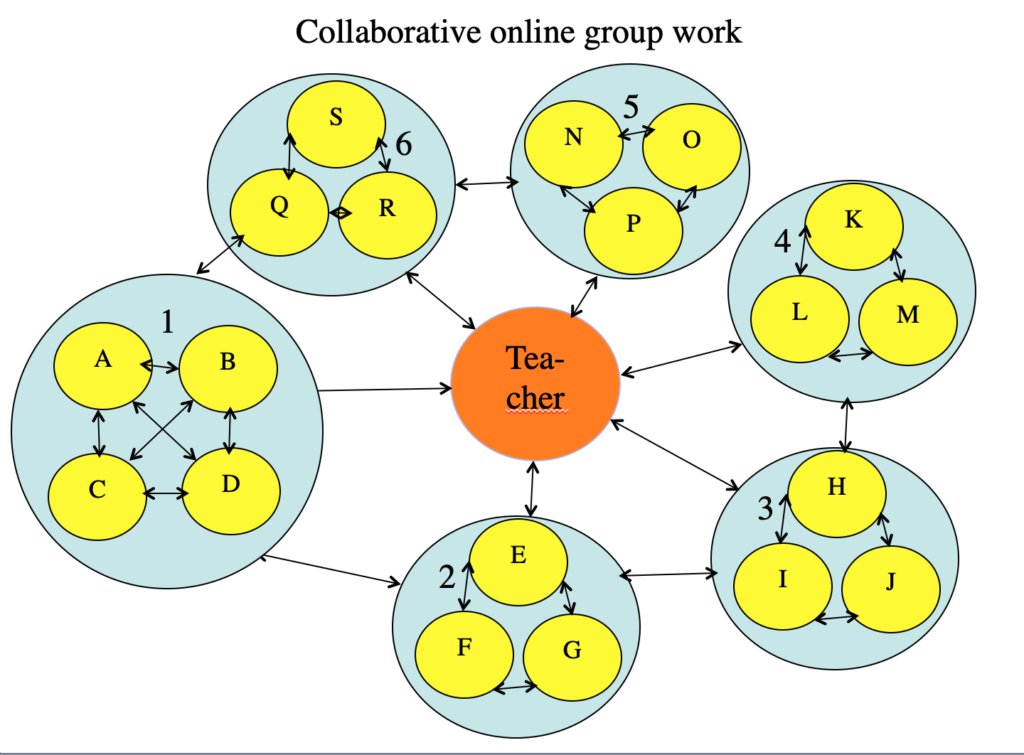
Figure 4.4.1. Collaborative group work. In this example the teacher has organized a class of 19 students into six groups. The teacher can interact with individual students or with each group as a whole. In online collaborative learning each group can have its own online discussion area which can be ‘closed’ (except to the teacher) or open to the other students. In this model, all communication is textual, over the Internet, using online discussion forum software (which comes as standard in most LMSs). However, the model could be applied to classroom teaching, or to video-conferencing, but usually with smaller numbers of students due to bandwidth restrictions. Each mode of delivery though will need its own variations in design for it to work well. Image: Tony Bates, 2019.
4.4.1 What is online collaborative learning?
The concurrence of both constructivist approaches to learning and the development of the Internet has led to a particular form of constructivist teaching, originally called computer-mediated communication (CMC), or networked learning, but which has been developed into what Harasim (2017) now calls online collaborative learning theory (OCL). She describes OCL as follows (p. 90):
OCL theory provides a model of learning in which students are encouraged and supported to work together to create knowledge: to invent, to explore ways to innovate, and, by so doing, to seek the conceptual knowledge needed to solve problems rather than recite what they think is the right answer. While OCL theory does encourage the learner to be active and engaged, this is not considered to be sufficient for learning or knowledge construction……In the OCL theory, the teacher plays a key role not as a fellow-learner, but as the link to the knowledge community, or state of the art in that discipline. Learning is defined as conceptual change and is key to building knowledge. Learning activity needs to be informed and guided by the norms of the discipline and a discourse process that emphasises conceptual learning and builds knowledge.
OCL builds on and integrates theories of cognitive development that focus on conversational learning (Pask, 1975), conditions for deep learning (Marton and Saljø, 1997; Entwistle, 2000), development of academic knowledge (Laurillard, 2001), and knowledge construction (Scardamalia and Bereiter, 2006).
From the very early days of online learning, some instructors have focused heavily on the communication affordances of the Internet (see for instance, Hiltz and Turoff, 1978). They have based their teaching on the concept of knowledge construction, the gradual building of knowledge mainly through asynchronous online discussion among students and between students and an instructor.
Online discussion forums go back to the 1970s, but really took off as a result of a combination of the invention of the WorldWide Web in the 1990s, high speed Internet access, and the development of learning management systems, most of which now include an area for online discussions. These online discussion forums have some differences though with classroom seminars:
- first, they are text based, not oral;
- second, they are asynchronous: participants can log in at any time, and from anywhere with an Internet connection;
- third, many discussion forums allow for ‘threaded’ connections, enabling a response to be attached to the particular comment which prompted the response, rather than just displayed in chronological order. This allows for dynamic sub-topics to be developed, with sometimes more than ten responses within a single thread of discussion. This enables participants to follow multiple discussion topics over a period of time.
4.4.2 Core design principles of OCL
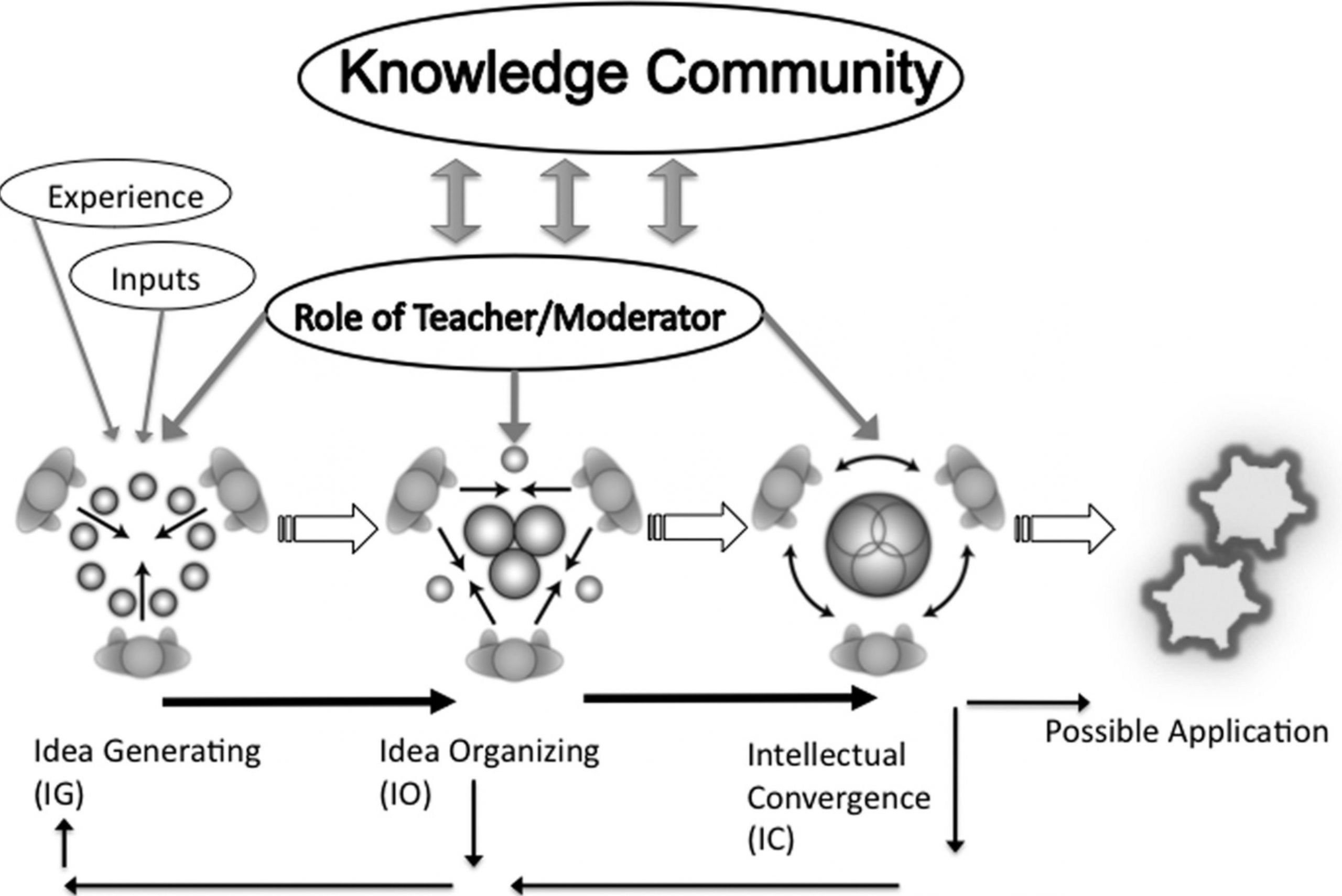
Harasim emphasises the importance of three key phases of knowledge construction through discourse:
- idea generating: this is literally brainstorming, to collect the divergent thinking within a group;
- idea organising: this is where learners compare, analyse and categorise the different ideas previously generated, again through discussion and argument;
- intellectual convergence: the aim here is to reach a level of intellectual synthesis, understanding and consensus (including agreeing to disagree), usually through the joint construction of some artefact or piece of work, such as an essay or assignment.
This results in what Harasim calls a Final Position, although in reality the position is never final because for a learner, once started, the process of generating, organising and converging on ideas continues at an ever deeper or more advanced level. The role of the teacher or instructor in this process is seen as critical, not only in facilitating the process and providing appropriate resources and learner activities that encourage this kind of learning, but also, as a representative of a knowledge community or subject domain, in ensuring that the core concepts, practices, standards and principles of the subject domain are fully integrated into the learning cycle.
Harasim provides the following diagram to capture this process:
Another important factor is that in the OCL model, discussion forums are not an addition or supplement to core teaching materials, such as textbooks, recorded lectures, or text in an LMS, but are the core component of the teaching. Textbooks, readings and other resources are chosen to support the discussion, not the other way round.
This is a key design principle, and explains why often instructors or tutors complain, in more ‘traditional’ online courses, that students don’t participate in discussions. Often this is because where online discussions are secondary to more didactic teaching, or are not deliberately designed and managed to lead to knowledge construction, students see the discussions as optional or extra work, because they have no direct impact on grades or assessment.
It is also a reason why awarding grades for participation in discussion forums misses the point. It is not the extrinsic activity that counts, but the intrinsic value of the discussion that matters (see, for instance, Brindley, Walti and Blashke, 2009). Thus although instructors using an OCL approach may use learning management systems for convenience, they are used differently from courses where traditional didactic teaching is moved online (as in 4.2.3).
4.4.3 Community of Inquiry
The Community of Inquiry Model (CoI) is somewhat similar to the OCL model. As defined by Garrison, Anderson and Archer (2000):
An educational community of inquiry is a group of individuals who collaboratively engage in purposeful critical discourse and reflection to construct personal meaning and confirm mutual understanding.
Garrison, Anderson and Archer argue that there are three essential elements of a community of inquiry:
- social presence: is “the ability of participants to identify with the community (e.g., course of study), communicate purposefully in a trusting environment, and develop inter-personal relationships by way of projecting their individual personalities.”
- teaching presence: is “the design, facilitation, and direction of cognitive and social processes for the purpose of realizing personally meaningful and educationally worthwhile learning outcomes“
- cognitive presence: is “the extent to which learners are able to construct and confirm meaning through sustained reflection and discourse“.
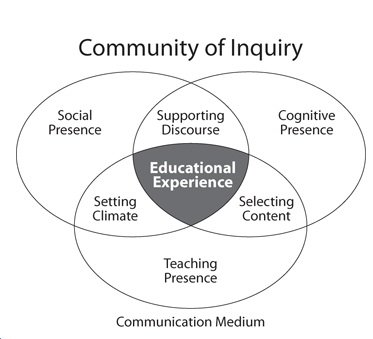
However, CoI is more of a theory than a model, since it does not indicate what activities or conditions are needed to create these three ‘presences’. The two models (OCL and CoI) are also more complementary rather than competing.
4.4.4 Developing meaningful online discussion
Since the publication of the original CoI paper in 2000, there have been a number of studies that have identified the importance of these ‘presences’ within online learning (click here for a wide selection). Although there has been a wide range of researchers and educators engaged in the area of online collaborative learning and communities of inquiry, there is a high degree of convergence and agreement about successful strategies and design principles. For academic and conceptual development, discussions need to be well organized by the teacher, and the teacher needs to provide the necessary support to enable the development of ideas and the construction of new knowledge for the students.
Partly as a result of this research, and partly as the result of experienced online instructors who have not necessarily been influenced by either the OCL or the Community of Inquiry literature, several other design principles have been associated with successful (online) discussion, such as:
- appropriate technology (for example, software that allows for threaded discussions);
- clear guidelines on student online behaviour, such as written codes of conduct for participating in discussions, and ensuring that they are enforced;
- student orientation and preparation, including technology orientation and explaining the purpose of discussion;
- clear goals for the discussions that are understood by the students, such as: ‘to explore gender and class issues in selected novels’ or ‘to compare and evaluate alternative methods of coding’;
- choice of appropriate topics, that complement and expand issues in the study materials, and are relevant to answering assessment questions;
- setting an appropriate ‘tone’ or requirements for discussion (for example, respectful disagreement, evidence-based arguments);
- defining clearly learner roles and expectations, such as ‘you should log in at least once a week to each discussion topic and make at least one substantive contribution to each topic each week’;
- monitoring the participation of individual learners, and responding accordingly, by providing the appropriate scaffolding or support, such as comments that help students develop their thinking around the topics, referring them back to study materials if necessary, or explaining issues when students seem to be confused or misinformed;
- regular, ongoing instructor ‘presence’, such as monitoring the discussions to prevent them getting off topic or too personal, and providing encouragement for those that are making real contributions to the discussion, heading off those that are trying to hog or dominate the discussions, and tracking those not participating, and helping them to participate;
- ensuring strong articulation between discussion topics and assessment.
These issues are discussed in more depth by Salmon (2000); Bates and Poole (2003); and Paloff and Pratt (2005; 2007).
4.4.5 Cultural and epistemological issues
Students come to the educational experience with different expectations and backgrounds. As a result there are often major cultural differences in students with regard to participating in discussion-based collaborative learning that in the end reflect deep differences with regard to traditions of learning and teaching. Thus teachers need to be aware that there are likely to be students in any class who may be struggling with language, cultural or epistemological issues, but in online classes, where students can come from anywhere, this is a particularly important issue.
In many countries, there is a strong tradition of the authoritarian role of the teacher and the transmission of information from the teacher to the student. In some cultures, it would be considered disrespectful to challenge or criticize the views of teachers or even other students. In an authoritarian, teacher-based culture, the views of other students may be considered irrelevant or unimportant. Other cultures have a strong oral tradition, or one based on story-telling, rather than on direct instruction.
Online environments then can present real challenges to students when a constructivist approach to the design of online learning activities is adopted. This may mean taking specific steps to help students who are unfamiliar with a constructivist approach to learning, such as asking a student to send drafts to the instructor by e-mail for approval before posting a ‘class’ contribution. For a fuller discussion of cross-cultural issues in online learning, see Jung and Gunawardena (2014) and the journal Distance Education, Vol. 22, No. 1 (2001), the whole edition of which is devoted to papers on this topic.
4.4.6 Strengths and weaknesses of online collaborative learning
This approach to the use of technology for teaching is very different from the more objectivist approaches found in computer-assisted learning, teaching machines, and artificial intelligence applications to education, which primarily aim to use computing to replace at least some of the activities traditionally done by human teachers. With online collaborative learning, the aim is not to replace the teacher, but to use the technology primarily to increase and improve communication between teacher and learners, with a particular approach to the development of learning based on knowledge construction assisted and developed through social discourse. This social discourse furthermore is not random, but managed in such a way as to ‘scaffold’ learning:
- by assisting with the construction of knowledge in ways that are guided by the instructor;
- that reflect the norms or values of the discipline;
- that also respect or take into consideration the prior knowledge within the discipline.
Thus there are two main strengths of this model:
- when applied appropriately, online collaborative learning can lead to deep, academic learning, or transformative learning, as well as, if not better than, discussion in campus-based classrooms. The asynchronous and recorded ‘affordances’ of online learning more than compensate for the lack of physical cues and other aspects of face-to-face discussion;
- online collaborative learning as a result can also directly support the development of a range of high level intellectual skills, such as critical thinking, analytical thinking, synthesis, and evaluation, which are key requirements for learners in a digital age.
There are though some limitations:
- it does not scale easily, requiring highly knowledgeable and skilled instructors, and a limited number of learners per instructor;
- it is more likely to accommodate to the epistemological positions of faculty and instructors in humanities, social sciences, education and some areas of business studies and health and conversely it is likely to be less accommodating to the epistemological positions of faculty in science, computer science and engineering. However, if combined with a problem-based or inquiry-based approach, it might have acceptance even in some of the STEM subject domains.
4.4.7 Summary
Many of the strengths and challenges of collaborative learning apply both in face-to-face or online learning contexts. It could be argued that there is no or little difference between online collaborative learning and well-conducted traditional classroom, discussion-based teaching. Although there are necessary adaptations depending on the mode of delivery, many of the core principles of successful collaborative learning (see Barkley, Major and Cross, 2014) will apply in both online and face-to-face teaching. Once again, we see that the mode of delivery is less important than the design model, which can work well in both contexts. Indeed, it is possible to conduct successful collaborative learning synchronously or asynchronously, at a distance or face-to-face.
However, there is plenty of evidence that collaborative learning can be done just as well online, which is important, given the need for more flexible models of delivery to meet the needs of a more diverse student body in a digital age. Also, the necessary conditions for success in teaching this way are now well known, even though they are not always universally applied.
References
Barkley, E., Major, C.H., and Cross, K.P. (2017) Collaborative Learning Techniques San Francisco: Jossey-Bass/Wiley
Bates, A. and Poole, G. (2003) Effective Teaching with Technology in Higher Education: Foundations for Success San Francisco: Jossey-Bass
Brindley, J., Walti, C. and Blashke, L. (2009) Creating Effective Collaborative Learning Groups in an Online Environment International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, Vol. 10, No. 3
Entwistle, N. (2000) Promoting deep learning through teaching and assessment: conceptual frameworks and educational contexts Leicester UK: TLRP Conference
Garrison, R., Anderson, A. and Archer, W. (2000) Critical Inquiry in a Text-based Environment: Computer Conferencing in Higher Education The Internet and Higher Education, Vol. 2, No. 3
Harasim, L. (2017) Learning Theory and Online Technologies 2nd edition New York/London: Taylor and Francis
Hiltz, R. and Turoff, M. (1978) The Network Nation: Human Communication via Computer Reading MA: Addison-Wesley
Jung, I. and Gunawardena, C. (eds.) (2014) Culture and Online Learning: Global Perspectives and Research Sterling VA: Stylus
Laurillard, D. (2001) Rethinking University Teaching: A Conversational Framework for the Effective Use of Learning Technologies New York/London: Routledge
Marton, F. and Saljö, R. (1997) Approaches to learning, in Marton, F., Hounsell, D. and Entwistle, N. (eds.) The experience of learning: Edinburgh: Scottish Academic Press (out of press, but available online)
Paloff, R. and Pratt, K. (2005) Collaborating Online: Learning Together in Community San Francisco: Jossey-Bass
Paloff, R. and Pratt, K. (2007) Building Online Learning Communities: Effective Strategies for the Virtual Classroom San Francisco: Jossey-Bass
Pask, G. (1975) Conversation, Cognition and Learning Amsterdam/London: Elsevier (out of press, but available online here)
Salmon, G. (2000) e-Moderating: The Key to Teaching and Learning Online London: Taylor and Francis
Scardamalia, M. and Bereiter, C. (2006) Knowledge Building: Theory, pedagogy and technology in Sawyer, K. (ed.) Cambridge Handbook of the Learning Sciences New York: Cambridge University Press
Activity 4.4: Evaluating online collaborative learning models
1. Can you see the differences between ‘Open Collaborative Learning’ (OCL) and ‘Communities of Inquiry’? Or are they really the same model with different names?
2. Do you agree that either of these models can be applied just as successfully online or face-to-face?
3. Do you see other strengths or weaknesses with these models?
4. Is this common sense dressed up as theory?
5. Does it make sense to apply either of these models to courses in the quantitative sciences such as physics or engineering? If so, under what conditions?
For my comments on these questions, click on the podcast below:

