D

Audio
Listen to an audio version of this page (3 min 8 sec):
Data
|
(1) nȏkanwa
|
|
Definition: Information that is collected first or second-hand. Data are usually numerical, organized in charts and displayed by graphs [1].
Example of Data
In 2021, 237,420 people reported speaking an Indigenous language well enough to conduct a conversation in Canada. Among them, 86,475 (approximately 36%) speak Cree languages [9].
Denominator
|
nichi akihtāson |
|
Definition: The number below the line in a fraction that can state one of the following: the number of elements in a set or the number of equal parts into which the whole is divided [1].

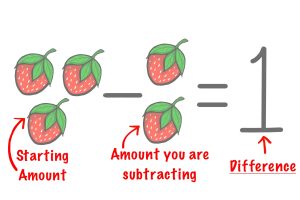
Difference
|
iskonikīwin |
|
Definition: It is the amount remaining after one quantity is subtracted from another [1].
Different
|
pȋtos |
|
Definition: Not alike in character or quality; distinct in nature; dissimilar [6].

Digit
|
peyak akihtâson |
|
Definition: A digit is a symbol used to contract numbers. It is any of the ten numerals: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9 [1].
Example of Digits
Three digits “3”, ‘0″, and “5” form the number “305”.
Dime
|
mitahsonias |
|
Definition: A small coin that is worth 10 cents. There are 10 dimes in a dollar [4].

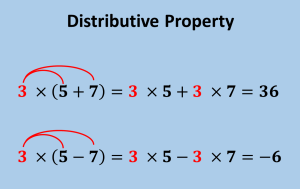
Distributive
|
(1) pēyakwan ayitaw
(2) ispȋhtawa-kēyhtakwanwah |
|
Definition: It is a property of real numbers that states that the product of the sum or difference of two numbers is the same as the sum or difference of their products [1].
Division
|
pahpiskihc âyâwin |
|
Definition: A mathematical operation involving two numbers that tells how many groups there are or how many are in each group [1].
Examples of Divisions
- [latex]18÷9=2[/latex]
- [latex]70÷5=14[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{30}{5}=6[/latex]
Dollar
|
pēyakwāpisk |
|
Definition: A dollar is a basic unit of money in many countries, such as the United States, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand [4].

Domain
|
itakisowina |
|
Definition: A domain is the set of all possible input values for a function or relation [4].