A

Audio
Listen to an audio version of this page (8 min 59 sec):
Absolute value
|
i-thikohk mwēci |
|
Definition: An integer’s absolute value is its distance from zero on the number line [8].

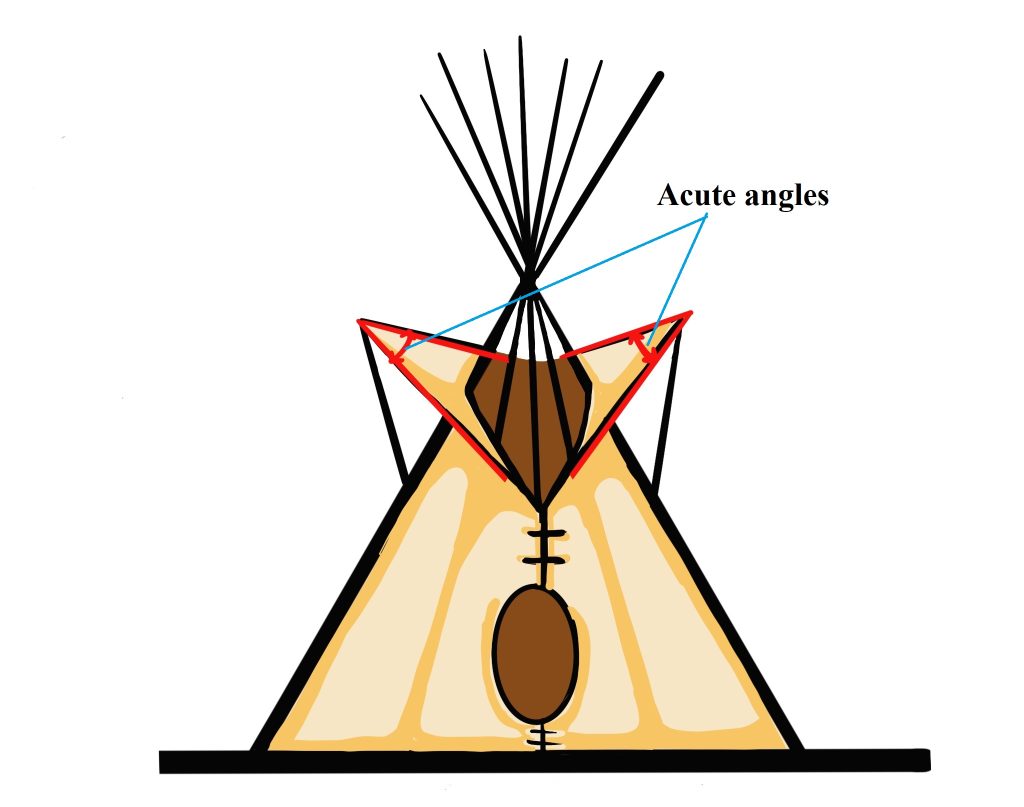
Acute angle
|
nōti-kahkahkīyaw |
|
Definition: An angle that measures less than 90 degrees [8].
Acute triangle
|
(1) otōskwana-nisto
|
|
Definition: An acute triangle has three angles that measure between 0 and 90 degrees [8].

Add
|
māmiwi-akihta |
|
Definition: It is a process to combine two or more quantities to find one quantity, called a total or a sum [1].
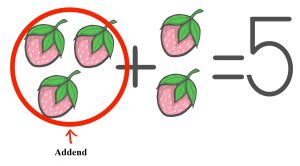
Addend
|
māmiwi-akihtasona |
|
Definition: Addends are numbers being added together [8].
Addition
|
takohakihcikewin |
|
Definition: It is a mathematical operation of combining two or more numbers into a sum [1].
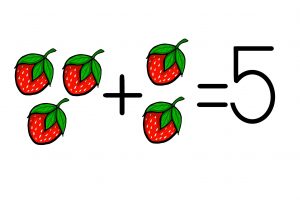
Addition property of equality
|
nāmawi-akicikiwin |
|
Definition: The property states that if you add the same number to both sides of an equation, the sides remain equal (i.e., the equation continues to be true) [8].
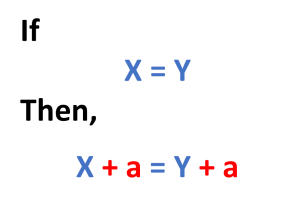
Additive inverse
|
tēyakwac |
|
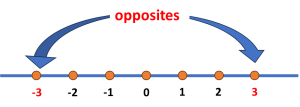
Definition: An additive inverse is the opposite of a given number [8].
Adjacent angles
|
(1) thikītakak (Woodland)
|
|
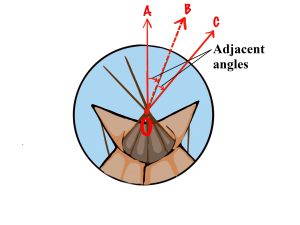
Definition: Adjacent angles are angles that are side by side and have a common vertex and ray [8].
Algebra
|
algebra |
|
Definition: Algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning the study of the rules of operations and relations, and the constructions and concepts arising from them, including terms, polynomials, equations and algebraic structure [8].
Algebraic equation
|
algebra oci masinayikiwin |
|
Definition: An algebraic equation is an equation that includes one or more variables [8].
Algebraic expression
|
algebra masinayikiwina |
|
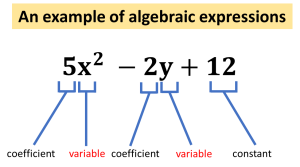
Definition: An algebraic expression is a mathematical expression that consists of variables, numbers and operations. The value of this expression can change.
Algebraic numbers
|
algebra akihcikewina |
|
Definition: An algebraic number is a number that is a root of a non-zero polynomial in one variable with rational coefficients [8].
Angle
|
(1) wīhkwētakāw
|
|
Definition: An angle is a figure formed by two rays that have a common endpoint. [8].
Angle measure
|
wīhkwētakāw kayispicak |
|
Definition: The size of an angle is measured in degrees [8].
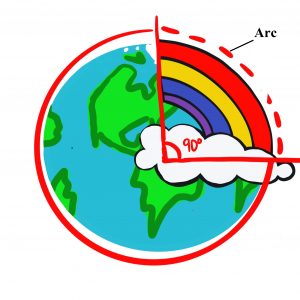
Arc
|
(1) wāki-yaw
|
|
Definition: An arc is a part of a circle named by its endpoints [8].
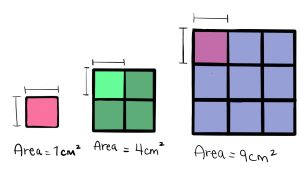
Area
|
askiy |
|
Definition: Area is the number of square units covering a closed figure [8].
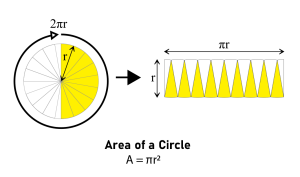
Area of a circle
|
pihcāyihk wāwiyiyaw |
|
Definition: The area of a circle is the number of square units inside that circle [8].
Area of a polygon
|
ka-tipastawa pihcāyihk |
|
Definition: The area of a polygon is the number of square units inside that polygon [8].
Arithmetic
|
akihtāsowēpinikēwin |
|
Definition: It is a branch of mathematics that studies the four operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) of positive numbers [8].
Arithmetic expression
|
akihtāsowēpinikēwina |
|
Definition: An algebraic expression is a mathematical expression that consists of numbers and arithmetic operators (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, roots, exponents, and parentheses).
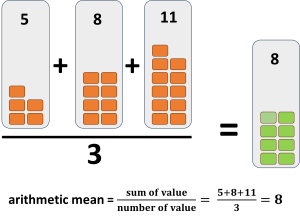
Arithmetic mean
|
akihtāsowēpinikēwin tastawāyak |
|
Definition: The arithmetic mean (also called the mean or average) of a list of numbers is the sum of all of the list divided by the number of items in the list [8].
Arithmetic operations
|
akihtāsowēpinikēwin itihwina |
|
Definition: The four basic arithmetic operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication and division [8].
Associative property
|
akihtāsowēpinikewin itwīwina |
|
Definition: It is a property of addition and multiplication that allows the numbers being added or multiplied to be regrouped without changing the outcome of the operations [3].

Average
|
tastawāyak |
|
Definition: The number obtained by dividing the sum of a set of numbers by the number of addends [8].
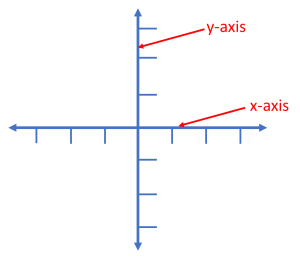
Axes
|
akask |
|
Definition: Axes are the horizontal number line (x-axis) and the vertical number line (y-axis) on the coordinate plane. Axes are also the lines at the side and bottom of a graph [8].