27 Style Guide
Before adapting an existing book, or creating a new one, it’s important to establish a road map that will guide the style of the work. This Style Guide, developed by the B.C. Open Textbook project, will provide a framework from which to begin. In addition to this guide, you can create a Style Sheet that outlines the specific characteristics of your book.
Manuals and Dictionaries
- Canadian Oxford Dictionary, 2nd ed.
- Editing Canadian English, 2nd ed.
For in-text citations and reference lists, consult style manual particular to the discipline of the specific book (e.g., MLA Handbook, APA, Chicago Manual of Style).
Citation Style
Select the citation style to be used for referencing material in your book and note this on your Style Sheet. If you are writing for a specific discipline, select the citation style appropriate for your area. If you are adapting an existing book, use the citation style chosen by the original author.
Use the citation style you’ve selected to set out rules for your book and record them in your Style Sheet to ensure consistency. Some basic questions to ask yourself:
- What will in-text citations look like?
- When inserting direct quotations, is a page number required?
- How will you list multiple authors for an in-text citation or entry in a reference list?
- Where will the reference list be located?
- Will you use footnotes instead of a reference list?
- How will you ensure that all in-text citations are noted in full in the reference list?
If you are creating a table, chart or graph, see “Citation vs Attribution” in Images: Captions, Attributions and Citations for information on how to add in-text citations.
If you are adapting a work and remove an in-text citation, remember to remove this reference from the reference list at the end of the chapter.
If you want to indicate sources used for writing that have not been specifically cited in the text, add these items to a Bibliography at the end of the chapter.
Pay close attention to the punctuation used for the citation style you’ve chose, such as:
- How periods are used
- Use of italics
- Use of brackets
- Use of quotation marks
- Use of spaces
Note: No periods should be used after URLs when they end a reference list entry.
Captions
See Images: Captions, Citations and Attributions
Spelling
In general, Canadian spellings should be used. Consult Canadian Spellings for first-choice spelling preferences. List any exceptions in your Style Sheet.
Punctuation
Consider how punctuation will be handled in your book. Below is one standard to use as a model. If you choose one or more different styles, enter these on your Style Sheet.
- Use a serial comma, i.e., a comma placed immediately before the coordinating conjunctive (and, or, nor) in a series of three or more terms.
- Serial comma: There were cows, horses, and pigs in the barn.
- No serial comma: There were cows, horses and pigs in the barn.
- Use commas in numerals over 999 (e.g., 1,000; 45,000)
- In displayed lists, always start items with a capital letter. Use end punctuation, such as a period, with full sentences only.
- Do NOT capitalize the first letter of the first word after a colon unless the colon introduces two or more sentences.
- With em dashes (inserted in Pressbooks by adding two hyphens side-by-side), insert a space on either side.
- Use the North American system for quotation marks: periods and commas always go inside quotation marks; semicolons and colons go outside.
- Use double quotes for all quoted matters. Single quotation marks should be reserved to enclose quotes within quotes. (e.g., Mark exclaimed, “You have driven a stake into my heart! Now I truly understand Caesar’s words, ‘Et tu Brute?’ How could you treat me so?”)
- Some exceptions to this system may be appropriate in specific disciplines. Please check with your project manager or copy editor.
- Place footnote numbers outside punctuation (usually a comma or period).
- Do not use periods in abbreviations, acronyms, and initialisms, except as noted in spelling list (e.g., et al., etc., i.e. are the most common that retain the periods).
- Do not hyphenate Latin phrases used adjectivally: ad hoc proposal, post hoc analysis.
- For hanging hyphen constructions (15- to 19-year-olds), do not hyphenate after “to.”
- Do not use quotes with so-called (e.g., Her so-called friend left her standing in the rain.)
Use of boldface
Boldface is reserved for key terms within the text body. It should not be used for emphasizing a word or phrase.
Use of italics
- Use italics for words used as words (e.g., The term vocal cords is often misspelled. What do you mean by nexus?)
- The titles of movies, TV shows, and radio programs are italicized (e.g., The Grey Fox, Definitely Not the Opera). The names of bands and music channels are regular font not italic (e.g., Bob’s Your Uncle, MuchMusic).
- See Italics and Foreign Words.
Dashes
Em dashes ( — )
- The em dash is the standard for breaking a sentence or setting off parenthetical statements.
- With em dashes, insert a space on either side.
- In Pressbooks, the em dash is created by using two hyphens. In the Book view, two hyphens will look like one long (em) dash.
En dashes (-)
- Use an en dash when expressing a range of years such as birth to death, e,g., 1955-2001.
- There should be no space on either side of the en dash.
- In Pressbooks, use one hyphen to indicate an one short (en) dash.
Spacing
Use only one space after a period (i.e., between sentences) and after a colon (:).
Italics and Foreign Words
Often foreign words are italicized in a textbook. However, if you’re not sure whether to use italics or not, consider the following:
- If the word is not italicized in the dictionary, then italics shouldn’t be used
- “Common” foreign words do not take italics (e.g. ad hoc, vis-a-vis)
- In Canadian English, many French words are not italicized.
If you’re not sure whether to use italics or not, do your best. Any errors will be picked up during the copy editing and proofing process.
Emphasizing Words with Punctuation
Sometimes an author will want to stress or emphasis a word or phrase. While acceptable, this practice should be kept to a minimum. In most cases, the word(s) should be written in a way that the stress or importance of a word or term is clear in context. Follow these guidelines:
- Do NOT use boldface or quotation marks for emphasis. Boldface is reserved for key terms within the text body.
- Use italics for words used as words (e.g., The term vocal cords is often misspelled. What do you mean by nexus?)
- Words that are meant to alert the reader that a term or word is used in nonstandard, ironic, or other special sense should be marked off with quotation marks (e.g., “Child protection” sometimes fails to protect).
- Words that are common expressions and figures of speech should NOT be set off in any way (and in this text, sometimes they are).
Measurements
Metric measurements should be used, i.e., km not miles; mm, cm and metres, not inches, feet or yards; kg not lbs; Celsius (C) not Fahrenheit (F).
If an existing book is being revised, convert imperial measurements to metric and round off the result. For example, 10 inches equals 25.4 cm. Record this as 25 cm.
Numbers
- Spell out numbers from one to nine and use arabic numerals for numbers greater than nine, except as indicated in checklist below.
- For ordinals, spell out first through ninth unless they are part of an array that includes a higher ordinal. Ordinals greater than ninth are expressed as numerals unless they occur at the beginning of a sentence (…in the 12th century but Twelfth-century monks…). Acceptable suffixes are 21st, 32nd, 43rd, 54th.
- Spell out fractions in running text with a hyphen (e.g., two-thirds).
- Use commas in numbers greater than 999.
- For percentages, use arabic numbers and the % symbol, closed up. The symbol should be repeated with each number in a range or series (the incidence varied from 1% to 4%; 6% to 7% of cases). If a sentence begins with a percent value, spell out both number and percent.
- For temperatures, use arabic numerals and the degree symbol (37.8°C).
- For times of day, use a colon only when a fraction of an hour is indicated (9:05 a.m.; otherwise 2 p.m.). With 12 o’clock, specify noon or midnight.
- For number ranges in text, use “to” (50 to 100 mg) except for years (1998–99, 1999–2013) and pages (213–223), which take en-dashes.
- For number ranges in tables and parentheses, use an en-dash (50–100 mg).
- Always use numerals with school grades (e.g., Grade 6).
- Use digits and abbreviations in measurements (e.g., puzzle boxes were 50 cm long, 38 cm wide, and 30 cm tall).
Use numerals rather than words
- In addresses (Suite 2, 400 West Hastings)
- For dates (17 May 1948)
- As designators (day 8, chapter 10, page 9, protocol 5)
- In figure and table designations (Figure 3, Table 6)
- For money ($14, $9.97, 6 cents, US$200)
- For temperatures (20°C)
- For time of day (11 p.m., 2:45 a.m., 07:30–13:00 )
- With units of measure (2 m, 7.2 kg)
- With percent symbols (0.02%, 99%)
- With “million” and “billion” ($1 million, 9.4 billion units)
Layout
Book
When you first begin working with your project manager, you’ll be asked to create an outline of your book. This outline should include a list of all chapters and their topics, as well as any front matter (introduction, preface) and back matter (appendices, glossary). Determining the outline, or layout, of the book helps to organize the subject matter and create a project timeline so the book can be appropriately managed.
Chapters and Boxes
Once you’ve created a book outline, consider the framework for each chapter and what is needed to address pedagogical concerns. The following items must be identified for your Style Sheet.
- Learning Objectives
- Key Takeaways (can be relabelled as Key Terms)
- Exercises (or related items such as Answers, Questions)
- Heading 2 title
- You can also highlight this information with a Text box (shaded or plain), found under Formats
Learning Objectives
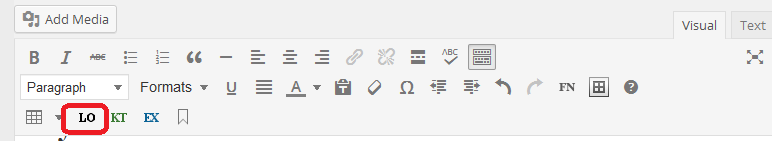
The Learning Objectives function is found at the top of the editing page. Click on “LO” to insert this box.
This is what the LO box looks like:
Learning Objectives
Type your learning objectives here.
- First
- Second
Key Takeaways
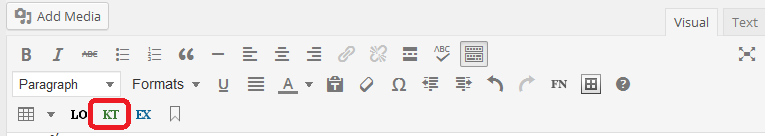
The Key Takeaways function is found at the top of the editing page. Click on “KT” to insert this box.
This is what the KT box looks like:
Key Takeaways
Type your key takeaways here.
- First
- Second
Key Terms (Glossary)
Typically, key terms are highlighted as bold or italicized in the text body and then added to the KT box. The term is set as bold in the KT box; the definition is in plain text.
The KT box function can be used to list Key Terms. Just relabel the box as so:
Key Terms
Type your key takeaways here.
- First
- Second
Exercises
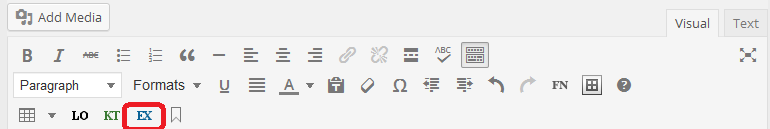
The Exercises function is found at the top of the editing page. Cick on “EX” to insert this box. The “Exercises” label for this box can be renamed using other synonyms for exercises that are descriptive of the type of exercises included such as “Short Answers”, “Exercises and Critical Thinking”, “Essays”.
This is what the EX box looks like:
Exercises
Type your exercises here.
- First
- Second
Headings
Pressbooks provides a variety of heading levels beginning with Heading 1 (the most prominent and largest) down to Heading 6.
- The default setting in Pressbooks defines the chapter title as H1, therefore all subsequent headings within a chapter should begin with H2.
- Create a hierarchy for the sections in your chapters and note which headings you’ve assigned to each in your Style Sheet.
- Decide how words in headings will be capitalized and record this decision in your Style Sheet as well.
Headings are important for accessibility, which we will explore more in the Accessibility Toolkit.
This is what the six different headings look like.
Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading 6
Style Sheet
Below is an example of a style sheet and what it should contain. Remember, list only exceptions and additions to the Style Guide. An area for pedagogical features has also been included.
| Style Item | Exception | Notes |
| Citation style | ||
| Spelling | ||
| Punctuation | ||
| Other style points | ||
| Pedagogical Features | Placement | Notes |
| Learning objectives | ||
| Key takeaways | ||
| Key terms/glossary | ||
| Exercises | ||
| Reference list | ||
| Suggested readings | ||
| Attributions | ||
| Appendices |